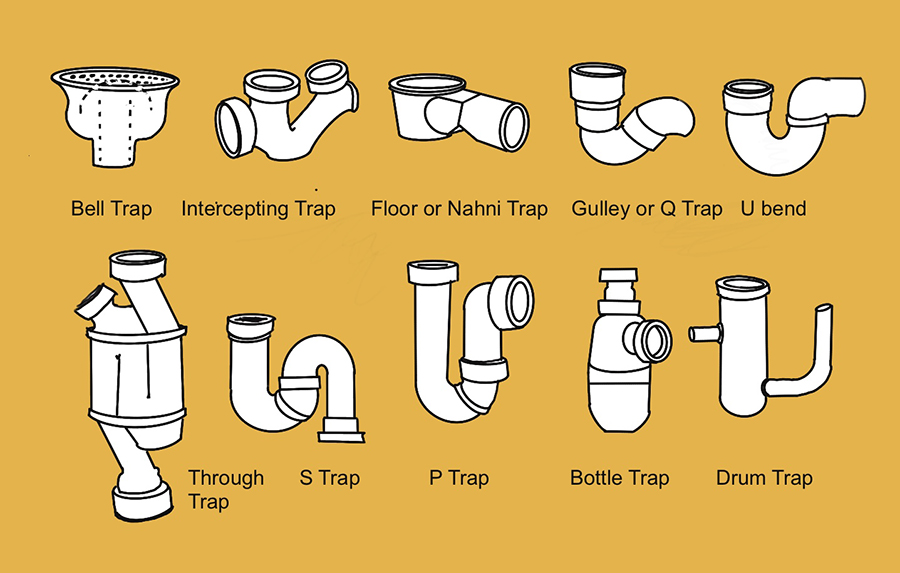
Types of waste trap
Contents |
[edit] What are waste traps?
Waste traps or traps are small plumbing devices designed to prevent odours from sewage or waste water leaving the pipe systems and entering the interior spaces of buildings. They can also help prevent the spread of bacteria and insects.
They are simple but ingenious devices that generally work by creating an air trap using the waste water of the system, which sits in a small reservoir within in the line of the waste water flow. It is normally a relatively simple plumbing part used in sinks, toilets, showers, baths as well as floor level drains, coming in a variety of types with various terms associated.
[edit] Types of waste trap
Some of the more common types of waste trap are described below.
[edit] U-bend
The U-bend is possibly the most common term used to describe a waste trap in the UK. The variations on this type all contain a U shaped form in their design. The U trap was invented by the English businessman plumber T.Crapper in the late 1800's and was an improvement on the S trap which was invented some 100 years earlier.
[edit] S trap
The S trap was invented by A.Cumming who also patented the first flush toilet, it developed into the U-bend, which was an improvement because it did not need an overflow pipe.
Shallow or low-level U-traps are based on the same system as the U-bend, but are shallow so that they fit into tight spaces such as underneath showers and bath units.
[edit] Gully or Q trap
A gully trap or Q trap has a basin in the ground with a water seal for odours and a vent pipe to allow fresh air in.
[edit] Floor or nahni trap
A floor or nahni trap is a shallow design of minimum 50 mm depth provided in the floor to drain and prevent smells entering internal spaces. Nahni is indian for washing area, where these are commonly used.
[edit] Interceptor trap
Interceptor traps normally act between the main sewer and building sewer, they have deep water seals of 100 mm to prevent bugs and insects crossing systems and are usually found in the outlet of the last manhole chamber from a property before the main sewer connection and are typically made of vitreous clay. There are many different types such as: The Winser trap, Kenon trap, Bristol trap, Buchan trap, Reverse Interceptor trap, The Radnor, The Netley (reverse action), The Warwick, The Coulsdon and The Salus.
[edit] Bell trap
A bell trap contains a water reservoir cup which has a bell shaped cover over it that dips at the edges into the water filled cup to form a seal.
[edit] Straight-through trap
A straight-through trap or through trap is a compact trap specifically allowing for neat plumbing behind basin pedestals.
[edit] P-trap
A P-trap is a u-shaped bend in a waste pipe,containing sitting water, that connects a sink's drain to a septic tank or main sewer system.
[edit] Bottle trap
A bottle trap is attached under a sink to block gases from rising from a drainage systems into a bathroom.
[edit] Drum trap
Drum traps are often found in older systems functioning in a similar way to bottle traps.
[edit] Other type or names for traps
Grease trap, running trap, low-level bath trap etc..
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
The Architectural Technology podcast: Where it's AT
Catch up for free, subscribe and share with your network.
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.